OpenAI’s recently launched GPT store potentially marks a significant shift in the global digital economy landscape, presenting a viable competitive threat to established platforms like Apple’s App Store. Competition in the global digital economy is all about creating platforms that bring different sides of a market together to create value. These shifts always appear significant with the benefit of hindsight but they start subtly if one knows where to look.
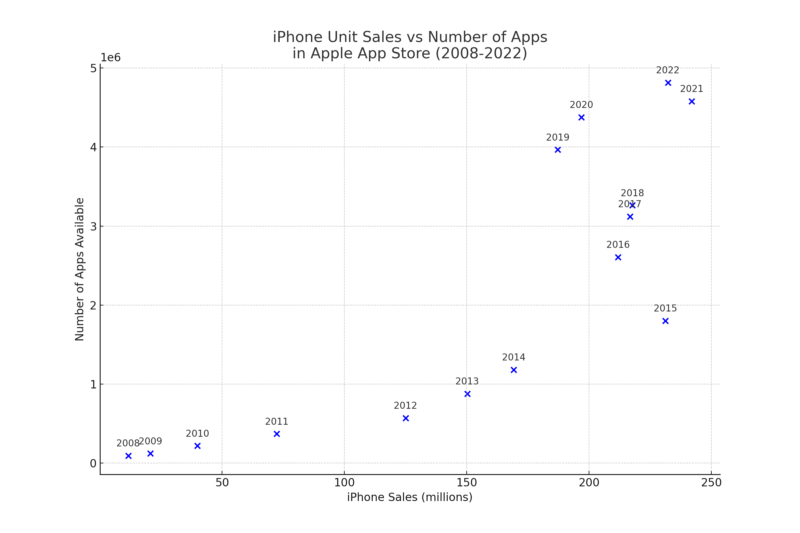
Apple launched its App Store in 2008. “Apps” were aggregations of data, compute, and algorithms designed to play nicely in the Apple iPhone ecosystem. Figure 1 below, based on data from Statista, traces the journey of iPhone sales versus the number of apps in Apple’s App Store from 2008 to 2022. The early years witnessed robust growth – iPhone sales and the number of apps grew exponentially. This surge symbolized a booming platform, innovating new technological solutions as more than a billion people became glued to their iPhone devices.
However, more recent trends paint a different picture. A noticeable slowdown in growth rates, both in terms of iPhone sales and app proliferation, began in the last decade suggesting a market approaching maturity. The once steep curve of expansion is now leveling off. Stable smartphone penetration rates imply that the majority of potential consumers are already reached, and the focus is shifting from market expansion to market retention (Did you upgrade to the latest iPhone?) and enhancement (How many apps on your iPhone? What new features does iOS offer?). Although the total number of apps continued to grow in the last decade, the rate of growth has decelerated. This slowdown can be attributed to market saturation, where the App Store has already amassed a vast number of applications, covering a wide array of functionalities and user needs.
In this context, the technological innovation of generative models based on the transformer architecture and the creation of the GPT store have emerged as significant disruptors. This new platform, bringing together GPT developers and users, is not merely an alternative; it could be a paradigm shift in how digital services are conceptualized, developed, and delivered. Data-driven machine learning techniques and chatbot interfaces providing feedback to natural language queries may come to reign supreme.
The GPT store has several potential advantages. First, by making massive datasets and computational power accessible at reasonable cost, OpenAI’s GPT store levels the playing field for developers. This breaks down barriers to entry and fosters innovation, allowing even smaller developers to create sophisticated applications, evident from OpenAI’s claims that more than 3 million users have created custom versions of ChatGPT. Second, ChatGPT-based applications are not tied to a specific hardware or software ecosystem. They can be accessed across various devices and browsers, removing the limitations imposed by platform-specific app stores. Third, the technology’s flexibility, from underlying foundational models to finely tuned, specialized instances, means it can be applied across a vast array of domains, from simple task automation to complex problem-solving, making it appealing to a broader audience.
The explosive growth of ChatGPT is a testament to the potential of this new platform. It’s not just an alternative to traditional apps; it’s a new way of thinking about and interacting with digital services. This positions the GPT store not just as a competitor but as a potential market leader, capable of reshaping the landscape of the digital economy even more than regulatory actions, such as the Department of Justice’s purported antitrust scrutiny of Apple’s App Store. The transformative impact of technological and industrial organizational innovation like the GPT store is likely to be more immediate and profound.